Android源码编译user版本默认开启adb调试
本文讲述了Android adb调试功能的架构,以及手机端adbd的启动过程。文末讲述了如何在Android编译user版本的过程中,实现自动开启adb调试功能。
1 adb框架
Android Adb 一共分为三个部分:adb、adb server、adbd,源码路径:system/core/adb。根据他们运行的地方不同,可以分为pc端和手机端两部分。
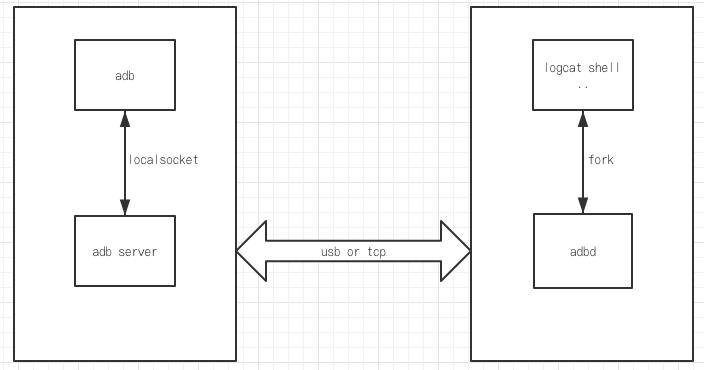
图1 adb架构
pc端
adb client和adb server 是运行在PC端,adb就是大家所熟悉的控制台命令adb,adb server是由adb fork出的一个常驻后台的子进程,作为adb的server进程,adb kill-server就是kill掉这个进程。adb与adb server 通过local socket进行通信
手机端
adbd运行在Android端,是在内核初始化完毕之后,由init进程启动。
2 adbd启动流程
手机端的adbd是在init解析rc文件的时候启动的,具体可以查看init.rc中的配置信息。根据注释,可以了解到adbd的启动是根据一个属性触发器来控制的,具体的触发器在init.<platform>.usb.rc文件中。
on property:ro.debuggable=1 start console # adbd is controlled via property triggers in init.<platform>.usb.rc service adbd /sbin/adbd --root_seclabel=u:r:su:s0 class core socket adbd stream 660 system system disabled seclabel u:r:adbd:s0 # adbd on at boot in emulator on property:ro.kernel.qemu=1 start adbd
接下来我们看看在init.<platform>.usb.rc文件中如何定义触发器。触发器根据sys.usb.config的值来决定是否启动adbd,其实就是仅当sys.usb.config的值中包含adb选项时才会启动adbd。
on property:sys.usb.config=ptp,adb
write /sys/class/android_usb/android0/enable 0
write /sys/class/android_usb/android0/idVendor 18D1
write /sys/class/android_usb/android0/idProduct 4EE6
write /sys/class/android_usb/android0/bDeviceClass 0
write /sys/class/android_usb/android0/bDeviceSubClass 0
write /sys/class/android_usb/android0/bDeviceProtocol 0
write /sys/class/android_usb/android0/functions ptp,adb
write /sys/class/android_usb/android0/enable 1
start adbd
setprop sys.usb.state ${sys.usb.config}
adbd的启动代码在system/core/adb/daemon/main.cpp中,其中main函数调用了adbd_main完成启动过程。adbd是一个linux程序,通过tcp或者usb与PC端的adb server通信,调用logcat shell等等程序实现各种调试功能。
int adbd_main(int server_port) { umask(0); signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); init_transport_registration(); // We need to call this even if auth isn't enabled because the file // descriptor will always be open. adbd_cloexec_auth_socket(); if (ALLOW_ADBD_NO_AUTH && !android::base::GetBoolProperty("ro.adb.secure", false)) { auth_required = false; } adbd_auth_init(); // Our external storage path may be different than apps, since // we aren't able to bind mount after dropping root. const char* adb_external_storage = getenv("ADB_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"); if (adb_external_storage != nullptr) { setenv("EXTERNAL_STORAGE", adb_external_storage, 1); } else { D("Warning: ADB_EXTERNAL_STORAGE is not set. Leaving EXTERNAL_STORAGE" " unchanged.\n"); } drop_privileges(server_port); bool is_usb = false; if (access(USB_FFS_ADB_EP0, F_OK) == 0) { // Listen on USB. usb_init(); is_usb = true; } // If one of these properties is set, also listen on that port. // If one of the properties isn't set and we couldn't listen on usb, listen // on the default port. std::string prop_port = android::base::GetProperty("service.adb.tcp.port", ""); if (prop_port.empty()) { prop_port = android::base::GetProperty("persist.adb.tcp.port", ""); } int port; if (sscanf(prop_port.c_str(), "%d", &port) == 1 && port > 0) { D("using port=%d", port); // Listen on TCP port specified by service.adb.tcp.port property. setup_port(port); } else if (!is_usb) { // Listen on default port. setup_port(DEFAULT_ADB_LOCAL_TRANSPORT_PORT); } D("adbd_main(): pre init_jdwp()"); init_jdwp(); D("adbd_main(): post init_jdwp()"); D("Event loop starting"); fdevent_loop(); return 0; } int main(int argc, char** argv) { while (true) { static struct option opts[] = { {"root_seclabel", required_argument, nullptr, 's'}, {"device_banner", required_argument, nullptr, 'b'}, {"version", no_argument, nullptr, 'v'}, }; int option_index = 0; int c = getopt_long(argc, argv, "", opts, &option_index); if (c == -1) { break; } switch (c) { case 's': root_seclabel = optarg; break; case 'b': adb_device_banner = optarg; break; case 'v': printf("Android Debug Bridge Daemon version %d.%d.%d %s\n", ADB_VERSION_MAJOR, ADB_VERSION_MINOR, ADB_SERVER_VERSION, ADB_REVISION); return 0; default: // getopt already prints "adbd: invalid option -- %c" for us. return 1; } } close_stdin(); debuggerd_init(nullptr); adb_trace_init(argv); D("Handling main()"); return adbd_main(DEFAULT_ADB_PORT); }
3 adbd权限
刚才提到了adbd的启动过程,接下来我们看一下adbd启动过程中的权限处理,在adbd_main函数中调用了drop_privileges进行降权处理。因为由init启动的进程启动,所以同样拥有和init一样的root权限。root权限过高,如果不是非必要,就要进行降权处理。如果当ro_debuggable && adb_root为true时,可以不用降权,维持root权限。简而言之就是当ro.debuggable为1且ro.secure为0的时候不用降权。
static void drop_privileges(int server_port) { ScopedMinijail jail(minijail_new()); // Add extra groups: // AID_ADB to access the USB driver // AID_LOG to read system logs (adb logcat) // AID_INPUT to diagnose input issues (getevent) // AID_INET to diagnose network issues (ping) // AID_NET_BT and AID_NET_BT_ADMIN to diagnose bluetooth (hcidump) // AID_SDCARD_R to allow reading from the SD card // AID_SDCARD_RW to allow writing to the SD card // AID_NET_BW_STATS to read out qtaguid statistics // AID_READPROC for reading /proc entries across UID boundaries gid_t groups[] = {AID_ADB, AID_LOG, AID_INPUT, AID_INET, AID_NET_BT, AID_NET_BT_ADMIN, AID_SDCARD_R, AID_SDCARD_RW, AID_NET_BW_STATS, AID_READPROC}; minijail_set_supplementary_gids(jail.get(), arraysize(groups), groups); // Don't listen on a port (default 5037) if running in secure mode. // Don't run as root if running in secure mode. if (should_drop_privileges()) { drop_capabilities_bounding_set_if_needed(jail.get()); minijail_change_gid(jail.get(), AID_SHELL); minijail_change_uid(jail.get(), AID_SHELL); // minijail_enter() will abort if any priv-dropping step fails. minijail_enter(jail.get()); D("Local port disabled"); } else { // minijail_enter() will abort if any priv-dropping step fails. minijail_enter(jail.get()); if (root_seclabel != nullptr) { if (selinux_android_setcon(root_seclabel) < 0) { LOG(FATAL) << "Could not set SELinux context"; } } std::string error; std::string local_name = android::base::StringPrintf("tcp:%d", server_port); if (install_listener(local_name, "*smartsocket*", nullptr, 0, nullptr, &error)) { LOG(FATAL) << "Could not install *smartsocket* listener: " << error; } } } static bool should_drop_privileges() { #if defined(ALLOW_ADBD_ROOT) // The properties that affect `adb root` and `adb unroot` are ro.secure and // ro.debuggable. In this context the names don't make the expected behavior // particularly obvious. // // ro.debuggable: // Allowed to become root, but not necessarily the default. Set to 1 on // eng and userdebug builds. // // ro.secure: // Drop privileges by default. Set to 1 on userdebug and user builds. bool ro_secure = android::base::GetBoolProperty("ro.secure", true); bool ro_debuggable = __android_log_is_debuggable(); // Drop privileges if ro.secure is set... bool drop = ro_secure; // ... except "adb root" lets you keep privileges in a debuggable build. std::string prop = android::base::GetProperty("service.adb.root", ""); bool adb_root = (prop == "1"); bool adb_unroot = (prop == "0"); if (ro_debuggable && adb_root) { drop = false; } // ... and "adb unroot" lets you explicitly drop privileges. if (adb_unroot) { drop = true; } return drop; #else return true; // "adb root" not allowed, always drop privileges. #endif // ALLOW_ADBD_ROOT }
4 user版本默认开启adb以及root权限
修改ro.adb.secure和ro.secure属性
修改build/core/main.mk,修改ro.secure和ro.adb.secure位0,注释掉enable_target_debugging或者将其设置为true。
--- a/core/main.mk +++ b/core/main.mk @@ -239,11 +239,11 @@ enable_target_debugging := true tags_to_install := ifneq (,$(user_variant)) # Target is secure in user builds. - ADDITIONAL_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES += ro.secure=1 + ADDITIONAL_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES += ro.secure=0 ADDITIONAL_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES += security.perf_harden=1 ifeq ($(user_variant),user) - ADDITIONAL_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES += ro.adb.secure=1 + ADDITIONAL_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES += ro.adb.secure=0 endif ifeq ($(user_variant),userdebug) @@ -251,7 +251,7 @@ ifneq (,$(user_variant)) tags_to_install += debug else # Disable debugging in plain user builds. - enable_target_debugging := + # enable_target_debugging := endif # Disallow mock locations by default for user builds
修改selinux
修改system/core/init/init.cpp,将selinux_is_enforcing的返回值调整为false。这里还有另外一种改法,就是在Boardconfig.mk里面对BOARD_KERNEL_CMDLINE进行编辑,添加androidboot.selinux=permissive。
static bool selinux_is_enforcing(void) { return false; }
修改adb模块的android.mk文件
修改system/core/adb/Android.mk中的编译选项,允许adb root。
--- a/adb/Android.mk +++ b/adb/Android.mk @@ -350,9 +350,9 @@ LOCAL_CFLAGS := \ -D_GNU_SOURCE \ -Wno-deprecated-declarations \ -LOCAL_CFLAGS += -DALLOW_ADBD_NO_AUTH=$(if $(filter userdebug eng,$(TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT)),1,0) +LOCAL_CFLAGS += -DALLOW_ADBD_NO_AUTH=$(if $(filter user userdebug eng,$(TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT)),1,0 -ifneq (,$(filter userdebug eng,$(TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT))) +ifneq (,$(filter user userdebug eng,$(TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT))) LOCAL_CFLAGS += -DALLOW_ADBD_DISABLE_VERITY=1 LOCAL_CFLAGS += -DALLOW_ADBD_ROOT=1 endif
设置默认打开adb端口
配置device.mk或者devicecommon.mk,设置usb配置选项,添加adb功能。
--- a/common/DeviceCommon.mk +++ b/common/DeviceCommon.mk @@ -153,7 +153,7 @@ PRODUCT_DEFAULT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES += \ # Set default USB interface PRODUCT_DEFAULT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES += \ - persist.sys.usb.config=ptp + persist.sys.usb.config=ptp,adb PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES += \ persist.sys.modem.diag=,gser \